Abstract
Introduction: Transplant ineligible patients (pts) with R/R DLBCL have poor outcomes. Polatuzumab vedotin (pola) is an antibody drug conjugate that delivers the microtubule inhibitor MMAE to CD79b-expressing cells, including DLBCL (Dornan et al. Blood 2009). A P1b/2 study evaluating pola plus bendamustine (B) together with rituximab (R) or obinutuzumab (G) in R/R follicular lymphoma and R/R DLBCL is ongoing (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02257567). Previously we reported results from the P1b (pola + BR, pola + BG) and P2 expansion of pola + BG and showed that these regimens were tolerable (Matasar et al. EHA 2017). We now report results of the randomized DLBCL cohorts that compared pola + BR to BR.
Aims: The P2 primary aim was to assess the efficacy of pola + BR vs BR at PRA (primary response assessment: 6-8 weeks after last study treatment) by an independent review committee (IRC) using modified Lugano Classification (CR required PET negativity and bone marrow biopsy confirmation of clearance if positive at screening). Secondary aims included safety evaluation and investigator-assessed responses by PET/CT and CT alone. Exploratory aims included duration of response (DOR), PFS, OS, and biomarker analysis.
Methods: After informed consent, 80 R/R DLBCL pts were randomized to pola 1.8 mg/kg plus R (375 mg/m2) and B (90 mg/m2) or BR every 21 days for 6 cycles. Transplant eligible pts were excluded but pts could have had prior autologous but not allogeneic transplant. Pts were stratified by DOR to last prior treatment ≤12 months (mo) vs >12 mo.
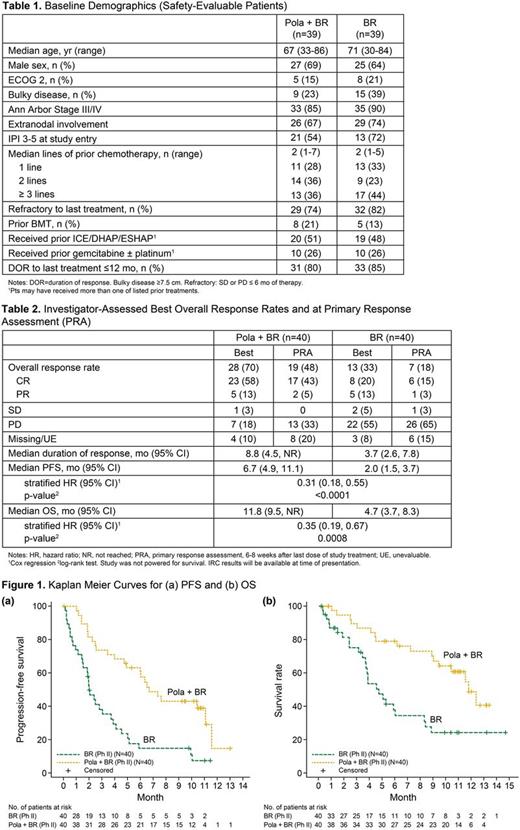
Results: Of 40 pts randomized to each arm, 39 pts in each arm received ≥1 treatment dose. Baseline characteristics of safety evaluable pts were comparable between the two arms (Table 1). As of 3 May 2017, median follow up for surviving pts was 10.9 mo for pola + BR and 7.6 mo for BR. Pola + BR pts completed more treatment cycles vs BR pts, with median of 5 vs 3 completed cycles, and 6 cycles completed by 46% vs 18% pts, respectively. Early treatment discontinuation due to PD occurred in 15% of pola + BR pts vs 54% of BR pts. AEs led to early treatment discontinuation in 33% pola + BR pts vs 10% BR pts. Safety: Non-heme AEs (all grades) occurring in >20% of pola + BR vs BR pts included diarrhea 41% vs 21%, infections 39% vs 41%, fatigue 36% vs 28%, pyrexia 33% vs 23%, nausea 26% vs 28%, decreased appetite 26% vs 15%, constipation 21% vs 18%, rash 10% vs 21%, and infusion related reactions 31% vs 21%. Heme AEs (all grades) in pola + BR vs BR were neutropenia 54% vs 39%, thrombocytopenia 49% vs 23%, and anemia 44% vs 15%, respectively. Peripheral neuropathy occurred in 39% pola + BR pts [21% Grade (Gr) 1, 18% Gr 2] vs 3% BR pts (3% Gr 2) and led to pola discontinuation in 1 pt and dose reduction in 2 pts. Gr 3-4 AEs occurring in >10 % of pts were infections (13% pola + BR vs 18% BR) and cytopenias. Gr 3-4 cytopenias were higher in pola + BR vs BR: neutropenia (46% vs 36%), thrombocytopenia (33% vs 21%), anemia (26% vs 13%) but were manageable with similar transfusion rates between the two arms. SAEs occurring in ≥ 10% of pts were infections (21% pola + BR vs 26% BR), febrile neutropenia (10% pola + BR vs 5% BR), and pyrexia (10% pola + BR vs 3% BR). Seven (18%) Grade 5 AEs occurred in each arm, including 3 (8%) in the setting of PD in each arm. Infection was the most common Gr 5 AE (3 per arm). Efficacy: Investigator-assessed best ORR and CR rates by PET/CT were higher in pola + BR vs BR with ORR 70% vs 33%, CR 58% vs 20% and at PRA with ORR 48% vs 18% and CR 43% vs 15%, respectively (Table 2). Median DOR for pola + BR vs BR was 8.8 mo vs 3.7 mo, respectively. Although the study was not powered for survival analyses, a significant benefit was seen in PFS and OS for pola + BR compared to BR (Figure 1). Median PFS for pola + BR vs BR was 6.7 mo (95% CI 4.9, 11.1) vs 2.0 mo (95% CI 1.5, 3.7) with stratified HR 0.31 (95% CI 0.18, 0.55) and p-value <0.0001 (calculated by Cox regression and log rank, respectively). Median OS for pola + BR vs BR was 11.8 mo (95% CI 9.5, NR) vs 4.7 mo (95% CI 3.7, 8.3) with stratified HR 0.35 (95% CI 0.19, 0.67) and p-value 0.0008. The OS benefit was proven to be consistent by subgroup and multivariate analyses. OS at 1 year for pola + BR was 48% vs 24% for BR. IRC, subgroup/multivariate analysis, and biomarker data will be updated at presentation.
Conclusion: Pola + BR increased response rates, prolonged PFS and OS and provided significant clinical benefit with manageable toxicity in this population with high unmet need. Further evaluation of this promising therapy is warranted.
Sehn: Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria. Herrera: Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Immune Design: Research Funding. Kamdar: Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau. McMillan: Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel sponsorship. Kim: J&J: Research Funding; Kyowa-Kirin: Research Funding; Celltrion, Inc: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Mundipharma: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Donga: Research Funding. Penuel: Genentech, Inc.: Employment. Cheng: F. Hoffman-La Roche Ltd: Employment. Hirata: Genentech, Inc.: Employment. Ku: Genentech, Inc.: Employment. Flowers: Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; Bayer: Consultancy; Burroughs Welcome Fund: Research Funding; V Foundation: Research Funding; National Cancer Institute: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Spectrum: Consultancy; Research to Practice: Research Funding; Educational Concepts: Research Funding; Prime Oncology: Research Funding; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; OptumRx: Consultancy; Clinical Care Options: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; National Institutes Of Health: Research Funding; Millennium/Takeda: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Onyx: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal